Forex
Divergence Cheat Sheet (2025): A Go-To Guide for Traders
Written by Sarah Abbas
Fact checked by Antonio Di Giacomo
Updated 28 January 2025

Table of Contents
Divergence occurs when the price of an asset moves in the opposite direction of a technical indicator, suggesting a potential change in trend. This 2025 divergence cheat sheet will break down the different types of divergence pattern, from strong to hidden, and provide you with practical tips and advanced strategies for divergence trading.
Key Takeaways
-
Divergence in trading occurs when the price of an asset moves in the opposite direction of a technical indicator, suggesting a potential trend change.
-
Types of divergence patterns include strong, medium, weak, and hidden, each offering different reliability and trading signals.
-
Tools for identifying divergence include RSI, MACD, and Stochastic Oscillator, which help spot divergence patterns and improve trading decisions.
Try a No-Risk Demo Account
Register for a free demo and refine your trading strategies.
Open Your Free Account
What Is Divergence in Trading?
Divergence happens when the price of an asset moves in one direction, but an indicator, like RSI or MACD, moves in the opposite direction.
This difference between price and indicator can signal that the current trend might change soon. Traders use divergence patterns to spot potential reversals or continuations in the market.
For example:
-
In a bullish divergence, the price makes lower lows, but the indicator makes higher lows. This means that even though the price is dropping, the selling pressure is getting weaker, and an upward move might be coming.
-
In a bearish divergence, the price makes higher highs, but the indicator makes lower highs. This suggests that the buying strength is decreasing, and the price might drop soon.
How Divergence Affects Market Phases
Divergence can happen in different market phases:
-
In trending markets: Hidden divergence patterns help confirm that the trend will continue. For instance, in an uptrend, a bullish divergence might indicate that the trend is still strong.
-
In sideways markets: Regular divergence is useful for spotting reversals when the price is moving within a range without a clear direction.
Divergence Cheat Sheet: Types of Divergence
Divergence occurs when there is a discrepancy between the price movement and a technical indicator. Recognizing these patterns can provide valuable insights into potential reversals or continuations in the market. Let’s explore the different types of divergence in more detail.
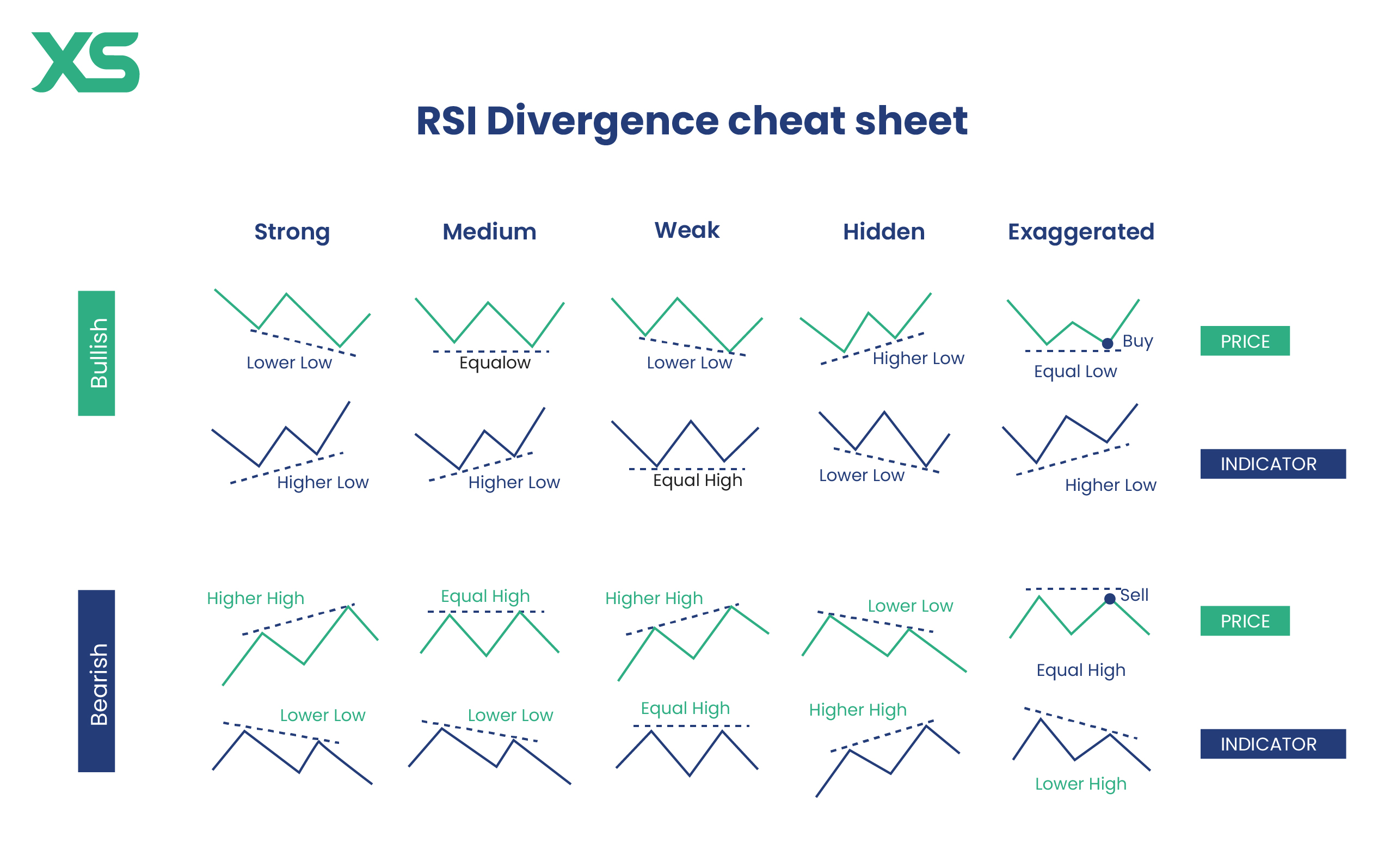
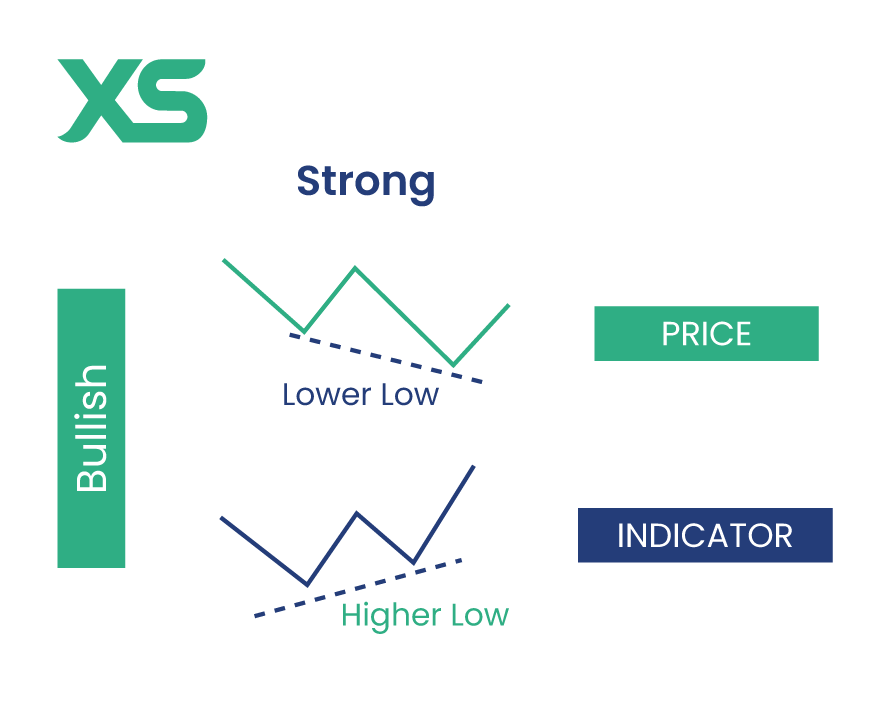
Strong Divergence
Strong divergence is the most reliable type of divergence, often signaling a significant reversal. It occurs when the price makes a new high or low, but the indicator fails to do so, indicating weakening momentum.
Bullish Strong Divergence
This happens when the price makes lower lows, but the indicator (like the RSI or MACD) makes higher lows. This suggests that the downward momentum is weakening, and an upward reversal is likely. Traders can use this signal to enter long positions as it indicates increasing buying pressure despite the lower price lows.
Imagine the price of a stock is making consecutive lower lows, but the RSI is making higher lows. This divergence suggests that although the price is falling, the momentum behind the sell-off is decreasing, hinting at a possible upward reversal.
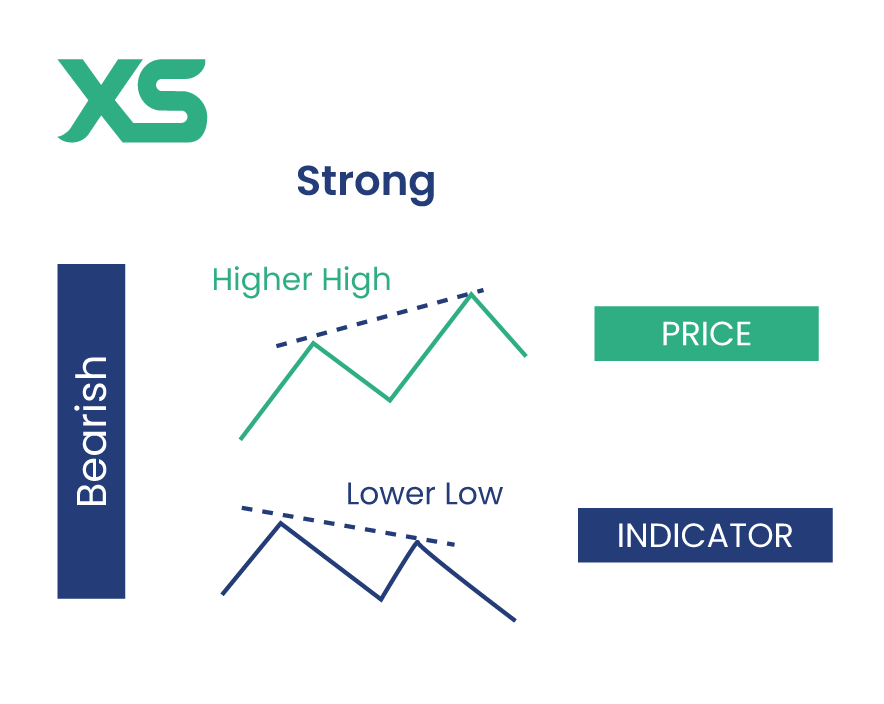
Bearish Strong Divergence
This occurs when the price makes higher highs, but the indicator makes lower highs. This signals that the upward momentum is waning, and a downward reversal could be coming.
Consider a scenario where the price of an asset is reaching new highs, but the MACD is showing lower highs. This bearish divergence indicates that the buying momentum is fading, potentially leading to a price drop.
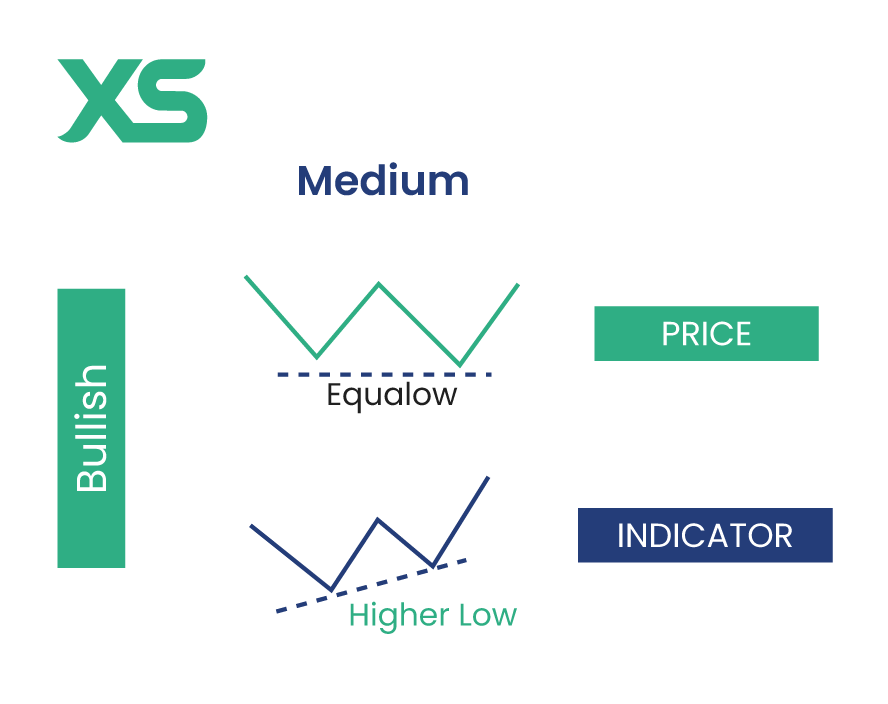
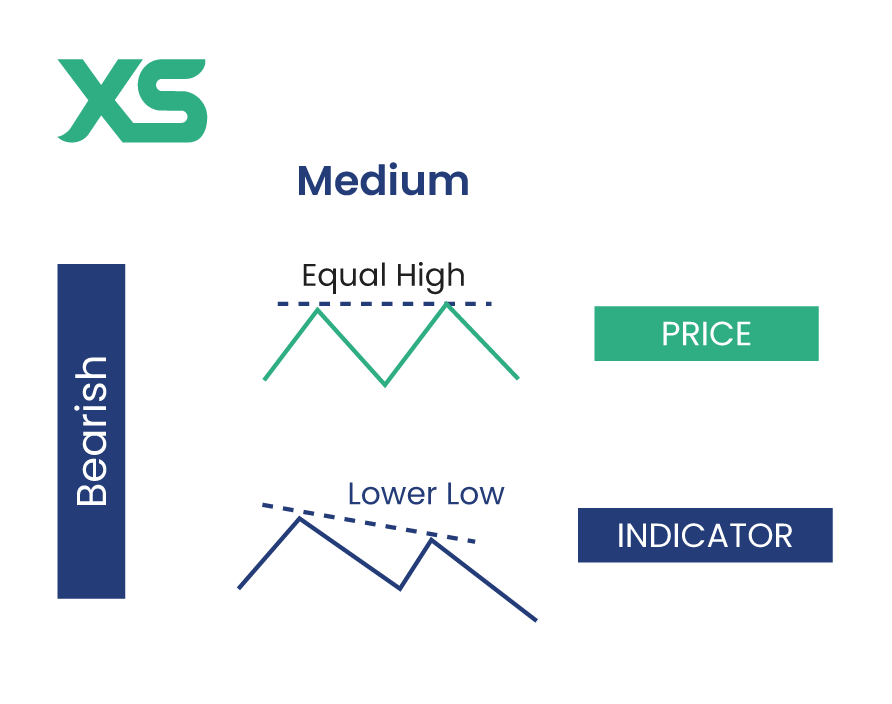
Medium Divergence
Medium divergence is less reliable than strong divergence but can still provide valuable trading signals. It occurs when the price and indicator move in the same direction but with a smaller degree of movement than the price.
Bullish Medium Divergence
The price and indicator both make lower lows, but the indicator's lows are not as pronounced as the price's lows. This suggests a potential reversal but with less certainty than a strong divergence.
If the price of a currency pair is falling and making lower lows while the RSI also makes lower lows but not as deep, this could indicate that the downtrend is losing strength, and a reversal might occur soon.
Bearish Medium Divergence
The price and indicator both make higher highs, but the indicator's highs are less pronounced. This hints at a potential downward reversal, though with less confidence.
When a commodity price rises and makes higher highs, but the MACD makes higher highs at a less steep angle, it suggests that the uptrend could be losing steam, and a price decline might follow.
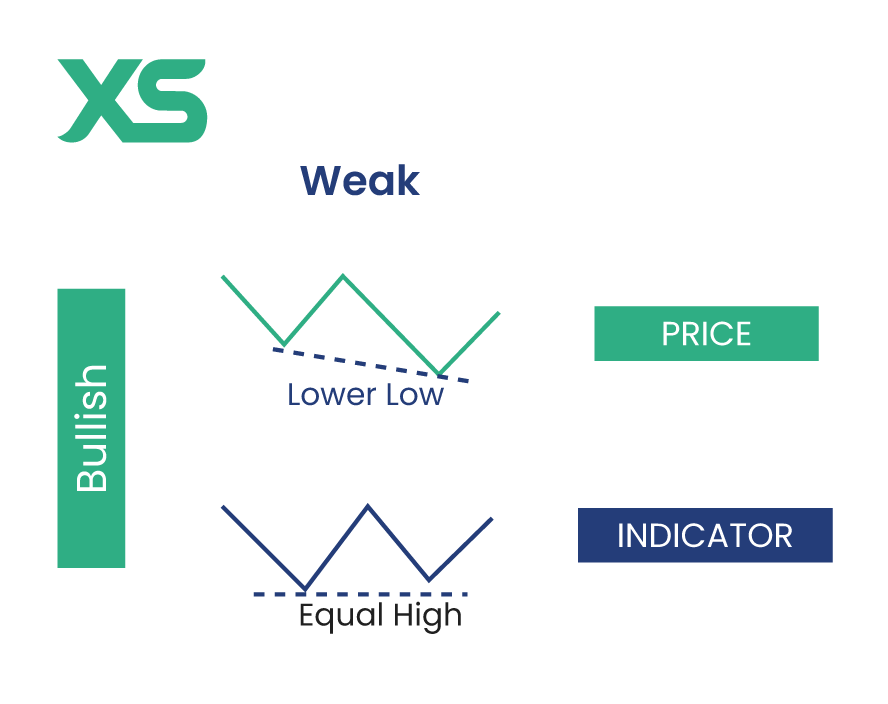
Weak Divergence
Weak divergence is the least reliable type and often occurs in trending markets. It happens when the price and indicator move in the same direction, but the indicator shows an even smaller movement than the price.
Bullish Weak Divergence
Both the price and indicator make lower lows, but the indicator's lows are much less pronounced. This type of divergence suggests a potential reversal, but it's weaker and should be confirmed with other signals.
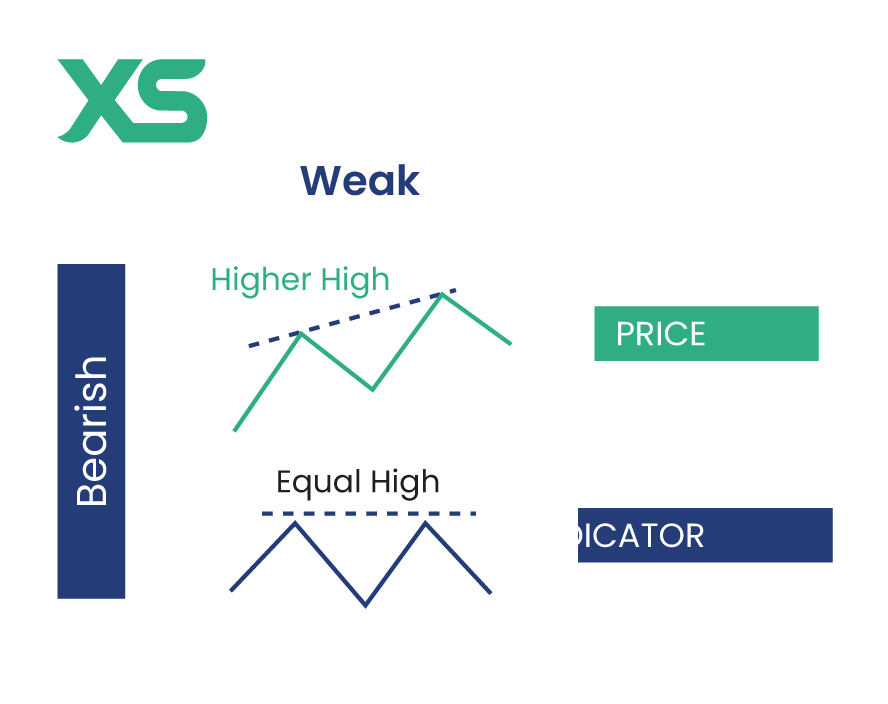
Bearish Weak Divergence
Both the price and indicator make higher highs, but the indicator's highs are much less pronounced. This indicates a possible downward reversal but is less reliable and should be used cautiously.
If the price of an index is making higher highs along with the MACD, but the MACD’s highs are barely higher, it suggests that the uptrend may be weakening, but this signal alone is not strong enough to act upon without additional confirmation.
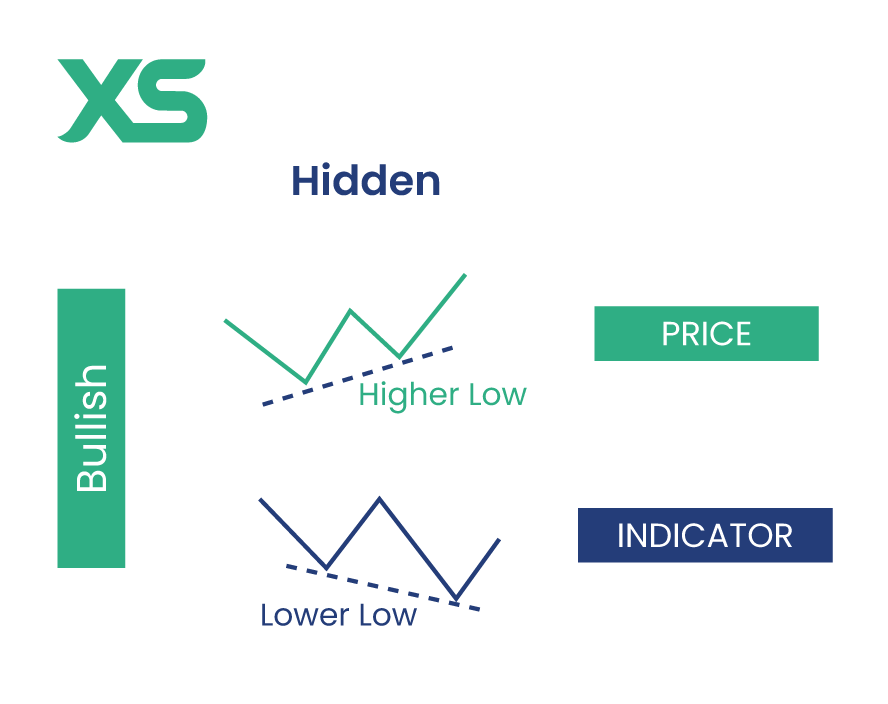
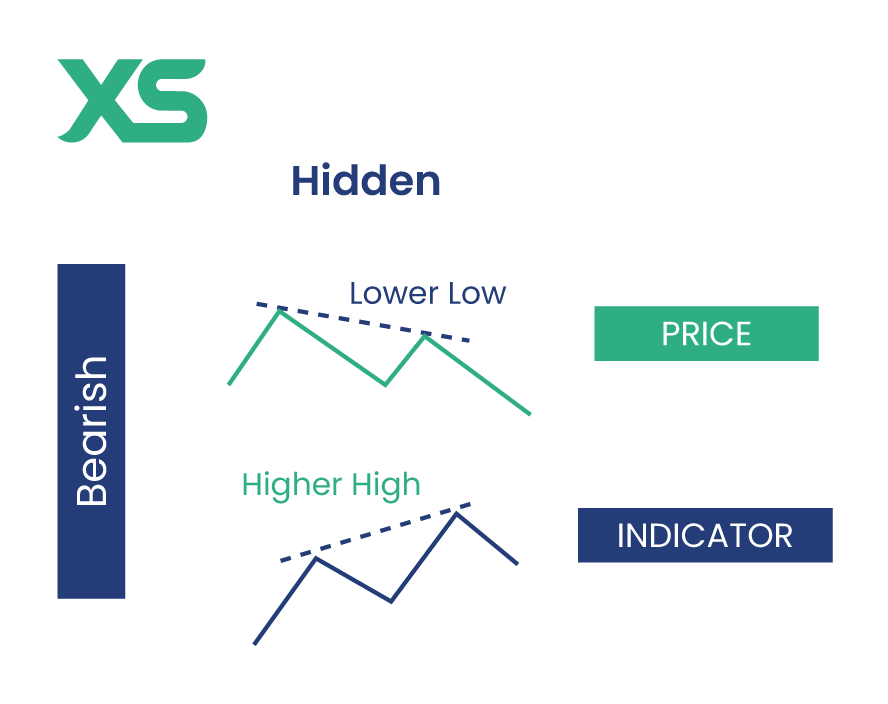
Hidden Divergence
Hidden divergence is a continuation signal, suggesting that the current trend will likely continue. It's often used to confirm the strength of a trend.
Bullish Hidden Divergence
This occurs when the price makes higher lows, but the indicator makes lower lows. This indicates that the underlying strength of the uptrend is still intact, suggesting further upward movement.
Suppose the price of an asset is in an uptrend, making higher lows while the RSI makes lower lows. This bullish hidden divergence indicates that the uptrend is likely to continue, offering traders a good opportunity to add to their long positions.
Bearish Hidden Divergence
This occurs when the price makes lower highs, but the indicator makes higher highs. This indicates that the underlying strength of the downtrend is still present, suggesting further downward movement.
Imagine an asset in a downtrend making lower highs while the MACD is making higher highs. This bearish hidden divergence signals that the downtrend is likely to continue, allowing traders to maintain or enter short positions.
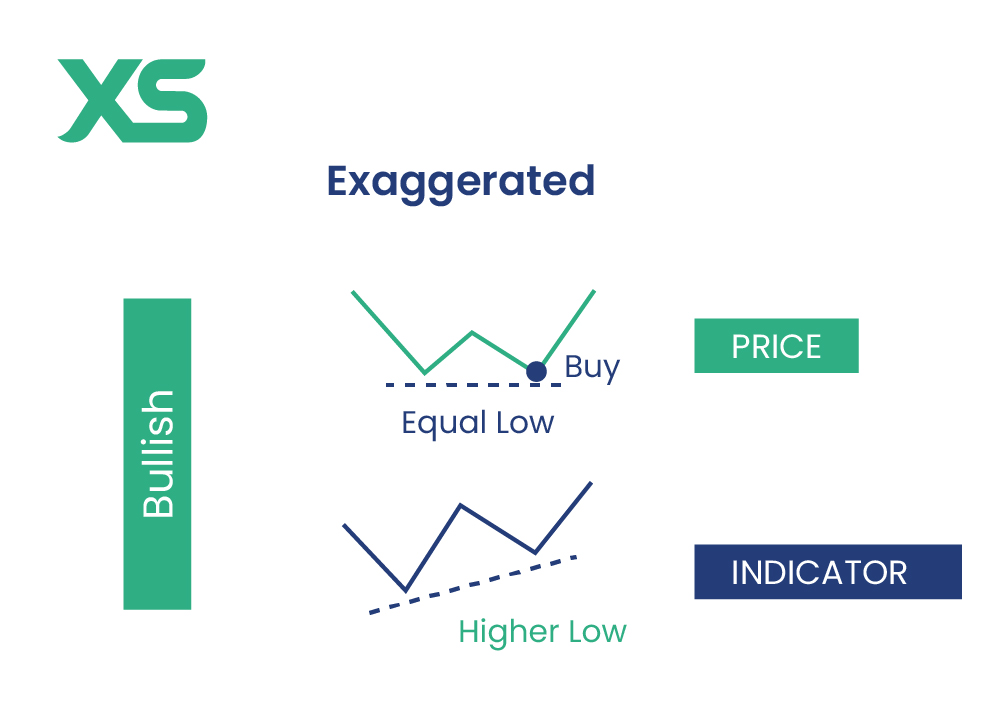
Exaggerated Divergence
Exaggerated divergence occurs when the price forms two equal highs or lows, while the indicator shows a discrepancy by making a lower high or higher low.
Though this type of divergence is often considered less reliable than strong divergence, it can still indicate a potential trend reversal, particularly in trending markets.
Bullish Exaggerated Divergence
Bullish exaggerated divergence happens when the price forms equal lows, but the indicator makes higher lows. This signals that despite the price maintaining a steady level, selling momentum is weakening, hinting at an upward reversal.
Imagine the price of a stock forms a double bottom (equal lows), but the RSI makes higher lows. This divergence suggests that although the price is flat, the downward pressure is diminishing, increasing the likelihood of a bullish reversal.
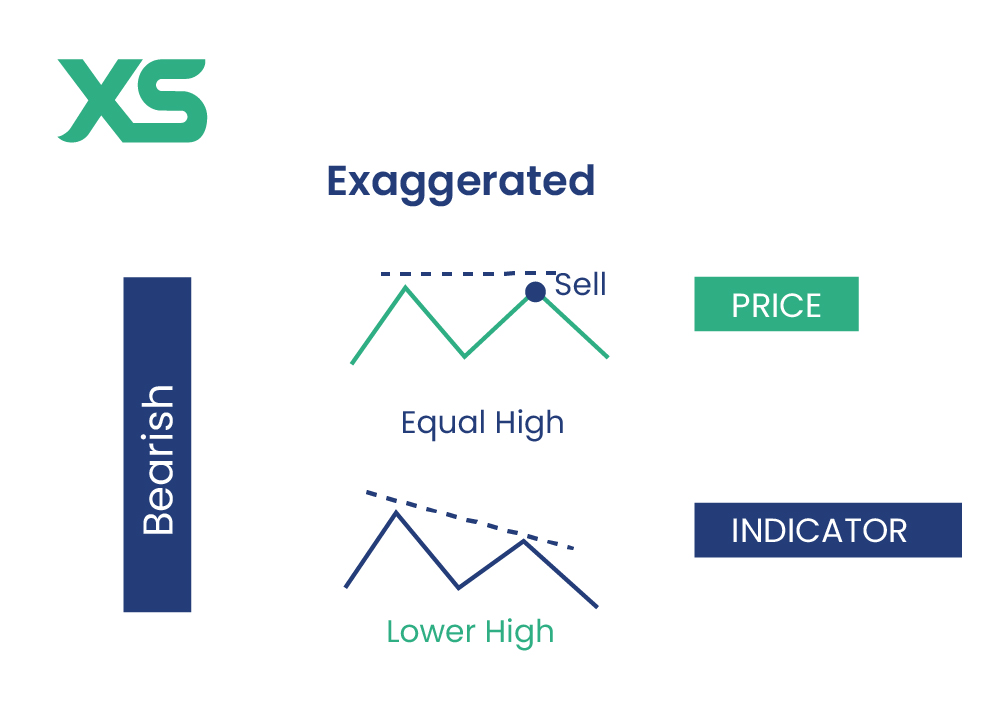
Bearish Exaggerated Divergence
Bearish exaggerated divergence occurs when the price forms equal highs, but the indicator shows lower highs. This indicates that buying momentum is fading, despite the price remaining at a peak, and suggests a potential downward reversal.
If a currency pair creates a double top (equal highs) while the MACD makes lower highs, this divergence suggests that buying pressure is weakening, signaling a likely price drop.
Reverse Divergence
Reverse divergence, also known as reverse regular divergence, occurs when the price moves in one direction, but the indicator shows the opposite. Instead of signaling a reversal, reverse divergence is typically used to confirm a trend continuation.
This type of divergence can help traders identify whether the current trend has the strength to persist.
Bullish Reverse Divergence
Bullish reverse divergence happens when the price makes higher highs, but the indicator makes lower highs. This indicates that the uptrend still has strength and is likely to continue despite the indicator's apparent weakening.
If the price of an asset makes new highs, but the RSI makes lower highs, this suggests that although the momentum seems to be weakening, the uptrend is still strong, and the price may continue rising.
Bearish Reverse Divergence
Bearish reverse divergence occurs when the price makes lower lows, but the indicator makes higher lows. This signals that the downtrend remains intact, despite the indicator showing signs of strength. It confirms that the bearish trend is likely to continue.
If a commodity's price makes lower lows while the MACD shows higher lows, this divergence signals that the downtrend is likely to persist, allowing traders to maintain or initiate short positions.
Tools for Identifying Divergence
Identifying divergence requires the use of technical indicators. Here are some of the most popular tools for spotting divergence patterns:
-
Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI measures the speed and change of price movements. It's a versatile tool for identifying divergence and overbought/oversold conditions.
-
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages. It's excellent for spotting divergence and understanding momentum shifts.
-
Stochastic Oscillator: This indicator compares an asset's closing price to a range of its prices over a certain period. It's useful for identifying divergence and potential reversal points.
Divergence vs. Convergence
While traders often focus on divergence patterns, it's also important to understand convergence and how it differs from divergence.
Both terms describe the relationship between price movements and indicators but signal different things about market trends.
What is Convergence?
Convergence happens when the price of an asset and an indicator, such as RSI or MACD, move in the same direction. This alignment confirms that the current trend is strong and likely to continue.
Unlike divergence, where the price and indicator disagree, convergence shows agreement between them.
For example:
- In an uptrend, both the price and the RSI are making higher highs. This suggests that the buying momentum is strong and the trend will likely continue.
-
In a downtrend, if both the price and MACD are making lower lows, it indicates that selling pressure is strong and the trend is still intact.
|
Feature |
Divergence |
Convergence |
|
Meaning |
Price and indicator move in opposite directions. |
Price and indicator move in the same direction. |
|
Implication |
Signals a possible trend reversal. |
Confirms the current trend continuation. |
|
Trader’s Action |
Look for potential entry/exit points. |
Stay with the current trend. |
|
Example |
Price makes higher highs, indicator makes lower highs (bearish divergence). |
Price and RSI both make higher highs in an uptrend. |
Advanced Divergence Strategies in 2025
Once you've mastered the basics of divergence, you can move on to more advanced strategies to enhance your trading.
Here’s an updated 2025 divergence trading strategy to look out for.
Multiple Timeframe Analysis
Using multiple timeframes to analyze divergence can provide a more comprehensive view of market conditions.
For instance, you might spot a strong divergence on a daily chart and confirm it with a shorter timeframe, like the hourly chart. This approach helps you align your trades with the overall market trend and improve entry and exit points.
Divergence in Different Market Conditions
Understanding how divergence behaves in different market conditions is crucial. In trending markets, hidden divergence can be particularly useful for confirming trend strength. In contrast, regular divergence is more effective in identifying reversals in ranging or consolidating markets.
For example, in a strong uptrend, spotting hidden bullish divergence can confirm the continuation of the trend, providing confidence to hold or add to a long position.
Conversely, in a ranging market, regular divergence can help identify potential breakouts or breakdowns.
Divergence and Volume Analysis
Combining divergence analysis with volume can provide additional confirmation of potential trend changes.
For example, if you spot a bullish divergence with increasing volume, it strengthens the signal that a reversal is likely. Conversely, a bearish divergence with decreasing volume can confirm a downward trend.
How to Use Divergence for Different Trading Styles
Divergence trading can be applied to various trading styles, helping traders spot potential trend changes or confirmations across different timeframes.
Scalping
Scalpers focus on quick trades, often within minutes. They use divergence charts on short timeframes (like 1-minute or 5-minute charts) to identify quick entry and exit points. Divergence trading helps scalpers catch small price reversals with indicators like RSI and MACD.
Swing Trading
Swing traders hold positions for days or weeks, looking for larger price movements. They rely on medium-term divergence charts to spot trend reversals and confirm continuation patterns. Using divergence trading with multiple indicators can provide stronger confirmation.
Day Trading
Day traders open and close positions within the same day, using divergence charts on hourly timeframes. They use divergence trading to identify intraday reversals and plan trades around market volatility.
Position Trading
Position traders take a long-term approach, holding trades for weeks or months. They use daily or weekly divergence charts to confirm long-term trends and avoid false signals. Divergence trading helps position traders stay in profitable trades longer.
Divergence Cheat Sheet: Tips
Here are some practical tips to help you effectively use divergence patterns in your trading:
-
Always confirm divergence signals with other technical indicators or chart patterns to increase reliability.
-
Protect your trades with stop-loss orders to manage risk, especially when trading weak or medium divergence.
-
Market conditions change, so regularly update your knowledge and adapt your strategies accordingly.
-
Divergence signals can sometimes take time to play out. Patience is key to successful divergence trading.
Conclusion
Understanding and applying divergence patterns in trading can significantly enhance your divergencestrategy. This Ultimate Divergence Cheat Sheet for 2025 has covered the different types of divergence, from strong to hidden, and provided you with the tools and tips to identify and trade these divergence patterns effectively.
Follow XS for more trading insights!

Get the latest insights & exclusive offers delivered straight to your inbox.
Table of Contents
FAQs
Yes, a divergence strategy can be profitable when used correctly, especially when combined with other technical analysis tools to confirm signals and manage risk effectively.
The best timeframe to spot divergence varies by trading style, but daily and 4-hour charts are commonly used for reliability, while shorter timeframes like 1-hour charts can be used for more frequent opportunities.
The best RSI setting for spotting divergence is typically 14 periods, but some traders prefer adjusting to 9 or 21 periods based on their specific trading strategy and timeframe.
Regular divergence signals a potential trend reversal when the price and indicator move in opposite directions. Hidden divergence, on the other hand, suggests the current trend will continue, showing the trend is still strong.
You can avoid false signals by confirming divergence with other tools like support and resistance levels, trendlines, or volume indicators. Using more than one indicator, like combining RSI with MACD, can also help verify the signal.
Divergence works best in sideways or ranging markets, where price reversals are more likely. In strong trending markets, hidden divergence is usually more reliable for confirming trend continuation rather than spotting reversals.
This written/visual material is comprised of personal opinions and ideas and may not reflect those of the Company. The content should not be construed as containing any type of investment advice and/or a solicitation for any transactions. It does not imply an obligation to purchase investment services, nor does it guarantee or predict future performance. XS, its affiliates, agents, directors, officers or employees do not guarantee the accuracy, validity, timeliness or completeness of any information or data made available and assume no liability for any loss arising from any investment based on the same. Our platform may not offer all the products or services mentioned.












